In the fast-paced world of digital marketing, SEO (Search Engine Optimization) stands as a cornerstone for online visibility and success. But for newcomers and even seasoned marketers, the sheer volume of acronyms and specialized terms can feel like learning a new language. We believe that understanding the fundamentals is key to effective strategy. That's why we've compiled this comprehensive guide, explaining each crucial term you'll encounter in your SEO journey. Think of this as your personal dictionary, designed to empower you with the knowledge to navigate discussions, interpret reports, and build winning SEO campaigns.
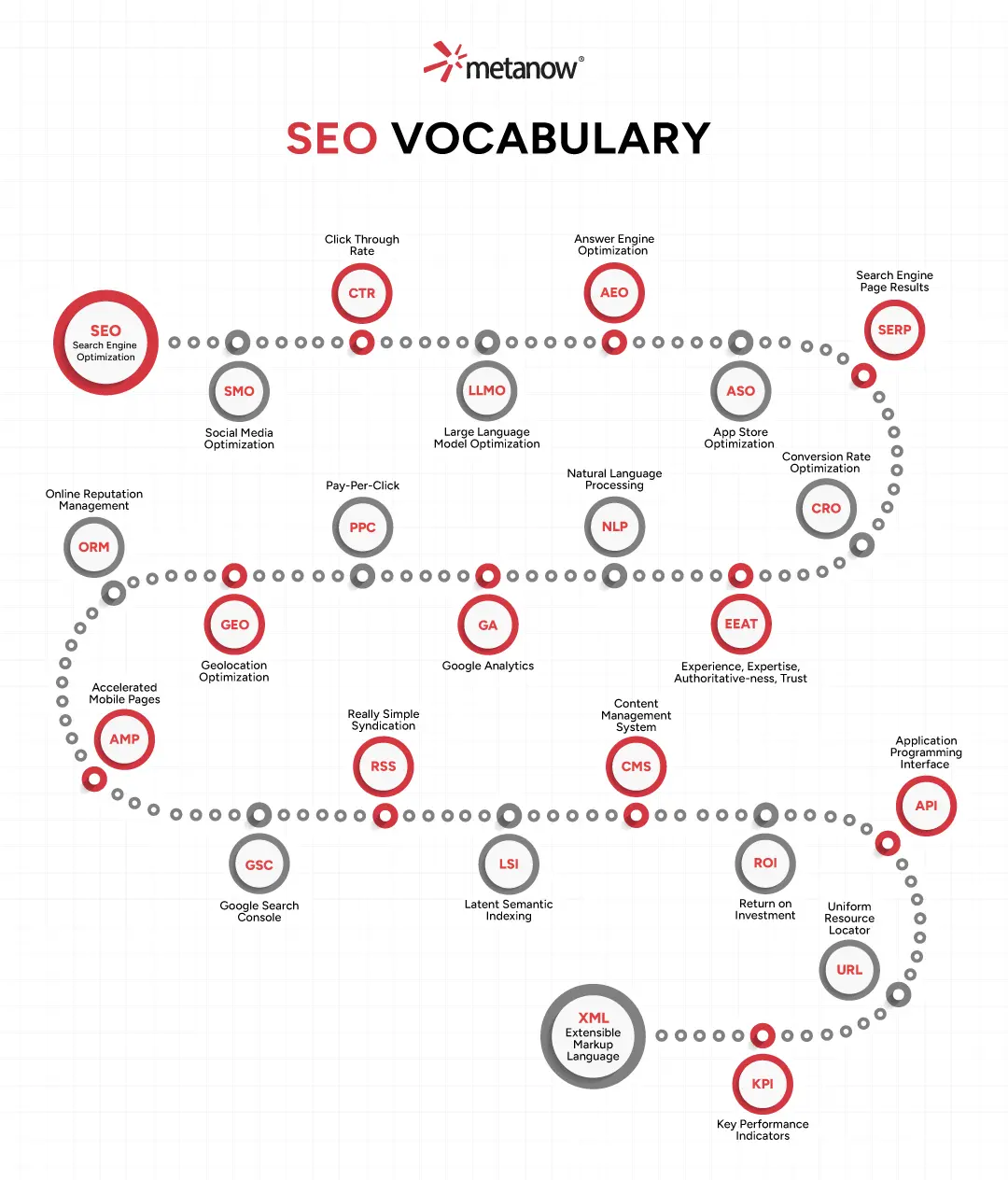
1. SEO (Search Engine Optimization)
- Definition: SEO is the practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results. It involves optimizing your website's content, structure, and technical aspects to rank higher on search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo.
- Why it Matters: Higher rankings mean more visibility, leading to more clicks, more potential customers, and ultimately, more business.
2. SERP (Search Engine Results Page)
- Definition: The SERP is the page displayed by a search engine in response to a user's query. It typically includes organic search results, paid ads, featured snippets, knowledge panels, and other rich results.
- Why it Matters: Your goal in SEO is to rank prominently on the SERP, ideally on the first page, to maximize visibility and clicks.
3. CTR (Click-Through Rate)
- Definition: CTR is the ratio of users who click on a specific link (e.g., your search result, ad, or email link) to the total number of users who view that link (impressions). It's usually expressed as a percentage.
- Formula: (Clicks / Impressions) * 100
- Why it Matters: A higher CTR indicates that your title tags, meta descriptions, or ad copy are compelling and relevant to searchers, encouraging them to visit your site.
4. CRO (Conversion Rate Optimization)
- Definition: CRO is the systematic process of increasing the percentage of website visitors who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, filling out a form, or signing up for a newsletter.
- Why it Matters: While SEO brings traffic, CRO ensures that traffic turns into tangible results. It's about making your website as effective as possible at converting visitors into customers or leads.
5. AEO (Answer Engine Optimization)
- Definition: AEO focuses on optimizing content to directly answer user queries, particularly for voice search, featured snippets, and conversational AI. It's about providing concise, direct answers that search engines can easily extract and present.
- Why it Matters: As voice search and AI assistants become more prevalent, optimizing for direct answers helps your content appear in "position zero" (featured snippets) and cater to how people increasingly search.
6. ASO (App Store Optimization)
- Definition: ASO is the process of optimizing mobile apps to rank higher in app store search results (e.g., Apple App Store, Google Play Store). It's essentially SEO for mobile apps.
- Why it Matters: Higher rankings in app stores lead to more visibility, more downloads, and ultimately, more users for your app.
7. ORM (Online Reputation Management)
- Definition: ORM involves monitoring, influencing, and improving how your brand or individual is perceived online. This includes managing reviews, social media mentions, news articles, and search engine results.
- Why it Matters: A positive online reputation builds trust, attracts customers, and can significantly impact your SEO, as search engines often factor in brand sentiment and authority.
8. SMO (Social Media Optimization)
- Definition: SMO refers to the use of social media platforms to increase the visibility of a product, brand, or event. While not direct SEO (social signals don't directly influence rankings), it drives traffic, builds brand awareness, and can lead to increased search queries for your brand.
- Why it Matters: Social media acts as a powerful amplifier for your content, extending its reach, encouraging shares, and indirectly supporting your SEO efforts by driving engagement and brand recognition.
9. PPC (Pay-Per-Click)
- Definition: PPC is an online advertising model where advertisers pay a fee each time one of their ads is clicked. It's a method of buying visits to your site, rather than earning those visits organically. Google Ads is the most popular PPC platform.
- Why it Matters: PPC offers immediate visibility and traffic, complements SEO by allowing you to target keywords you don't yet rank for organically, and provides valuable data for keyword research and conversion optimization.
10. LLMO (Large Language Model Optimization)
- Definition: LLMO is a newer concept focusing on optimizing content to be effectively understood and utilized by Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Gemini. This involves clear, concise, well-structured content that LLMs can easily process for summarization, answering questions, or generating new content.
- Why it Matters: As LLMs become integrated into search engines and AI assistants, optimizing for them ensures your content is accurately represented and leveraged in these evolving search landscapes.
11. NLP (Natural Language Processing)
- Definition: NLP is a branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to understand, interpret, and generate human language. In SEO, it's how search engines understand the meaning, context, and sentiment of content and search queries.
- Why it Matters: Understanding NLP helps SEOs create content that resonates with search engine algorithms, allowing them to accurately interpret the intent behind queries and the relevance of content.
12. GA (Google Analytics)
- Definition: Google Analytics is a free web analytics service offered by Google that tracks and reports website traffic. It provides insights into user behavior, traffic sources, content performance, and conversions.
- Why it Matters: GA is indispensable for measuring the success of your SEO efforts, identifying areas for improvement, and understanding your audience.
13. EEAT (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness)
- Definition: EEAT is a set of criteria Google's Search Quality Raters use to evaluate the quality of web pages. It emphasizes the importance of demonstrating real-world experience, deep expertise, strong authority in your niche, and a high level of trustworthiness.
- Why it Matters: Building strong EEAT signals is crucial for ranking well, especially for "Your Money Your Life" (YMYL) topics (e.g., health, finance), as Google prioritizes high-quality, reliable information.
14. GEO (Geolocation Optimization)
- Definition: GEO, or local SEO, involves optimizing your online presence to attract more local customers from relevant local searches. This includes optimizing your Google Business Profile, local citations, and location-specific keywords.
- Why it Matters: Essential for businesses with physical locations, local SEO ensures that when people in your vicinity search for your products or services, your business appears prominently.
15. AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
- Definition: AMP is an open-source HTML framework developed by Google to create fast-loading, lightweight mobile pages. AMP pages load almost instantly on mobile devices.
- Why it Matters: Faster loading times improve user experience, reduce bounce rates, and can positively influence mobile search rankings.
16. RSS (Really Simple Syndication)
- Definition: RSS is a web feed format used to publish frequently updated works, such as blog entries, news headlines, audio, and video, in a standardized format. Users can subscribe to RSS feeds to receive updates.
- Why it Matters: While less direct for SEO today, RSS can help distribute your content, notify subscribers of new posts, and contribute to content visibility and syndication.
17. GSC (Google Search Console)
- Definition: Google Search Console (formerly Google Webmaster Tools) is a free web service by Google that helps website owners monitor their site's performance in Google Search, identify and fix indexing issues, and understand search traffic.
- Why it Matters: GSC is a critical tool for SEOs, providing direct communication from Google about your site's health, ranking data, crawl errors, and much more.
18. CMS (Content Management System)
- Definition: A CMS is a software application or set of related programs used to create and manage digital content. Popular examples include WordPress, Joomla, and Shopify.
- Why it Matters: A well-chosen CMS can significantly impact your SEO efforts, offering features for easy content creation, metadata management, URL structuring, and overall site optimization.
19. LSI (Latent Semantic Indexing)
- Definition: LSI refers to a method used by search engines to understand the relationships between words and concepts. It's about finding related terms and synonyms that are semantically connected to your main keywords, rather than just exact matches.
- Why it Matters: Using LSI keywords helps search engines understand the depth and breadth of your content, showing that your page comprehensively covers a topic, which can improve rankings.
20. ROI (Return on Investment)
- Definition: ROI is a performance measure used to evaluate the efficiency or profitability of an investment. In SEO, it measures the financial benefit gained in relation to the money invested in SEO activities.
- Formula: (Net Profit from Investment / Cost of Investment) * 100
- Why it Matters: Proving ROI is essential for justifying SEO budgets and demonstrating the value of your efforts to stakeholders.
21. URL (Uniform Resource Locator)
- Definition: A URL is the address of a given unique resource on the web. It's what you type into your browser to access a website or a specific page.
- Why it Matters: SEO-friendly URLs are short, descriptive, contain keywords, and are easy for both users and search engines to understand.
22. API (Application Programming Interface)
- Definition: An API is a set of defined rules that enable different software applications to communicate with each other. In SEO, APIs are often used to pull data from various platforms (e.g., Google Search Console API, Google Analytics API) for reporting and analysis.
- Why it Matters: APIs allow for automation and integration of data, streamlining SEO workflows and enabling more sophisticated analysis and tool development.
23. XML (Extensible Markup Language)
- Definition: XML is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. In SEO, XML sitemaps are crucial.
- Why it Matters: An XML sitemap helps search engines crawl and index all the important pages on your website, especially for large sites or sites with complex navigation, ensuring that your content can be found.
24. KPI (Key Performance Indicator)
- Definition: A KPI is a measurable value that demonstrates how effectively a company is achieving key business objectives. In SEO, common KPIs include organic traffic, keyword rankings, conversion rate, bounce rate, and revenue from organic search.
- Why it Matters: KPIs provide a clear way to track progress, evaluate the success of your SEO strategies, and make data-driven decisions to optimize performance.
Conclusion
The world of SEO is dynamic, but a solid grasp of its core vocabulary is your ultimate starting point. By understanding these terms, you're not just learning jargon; you're gaining the power to communicate effectively, strategize intelligently, and ultimately, drive real results for your website and business.
Bookmark this guide, refer back to it often, and keep learning – the more fluent you become in SEO, the more successful your digital efforts will be!
Mastering the Language of SEO: Your Essential Vocabulary Guide